What is Heat Treatment?
Heat treatment is a controlled heating and cooling process used to alter the physical and mechanical properties of metals without changing their shape. It helps achieve the desired balance between strength, hardness, ductility, and toughness.
Different metals and industrial applications require specific heat treatment techniques. Below, we will explain the five major types of heat treatment processes.
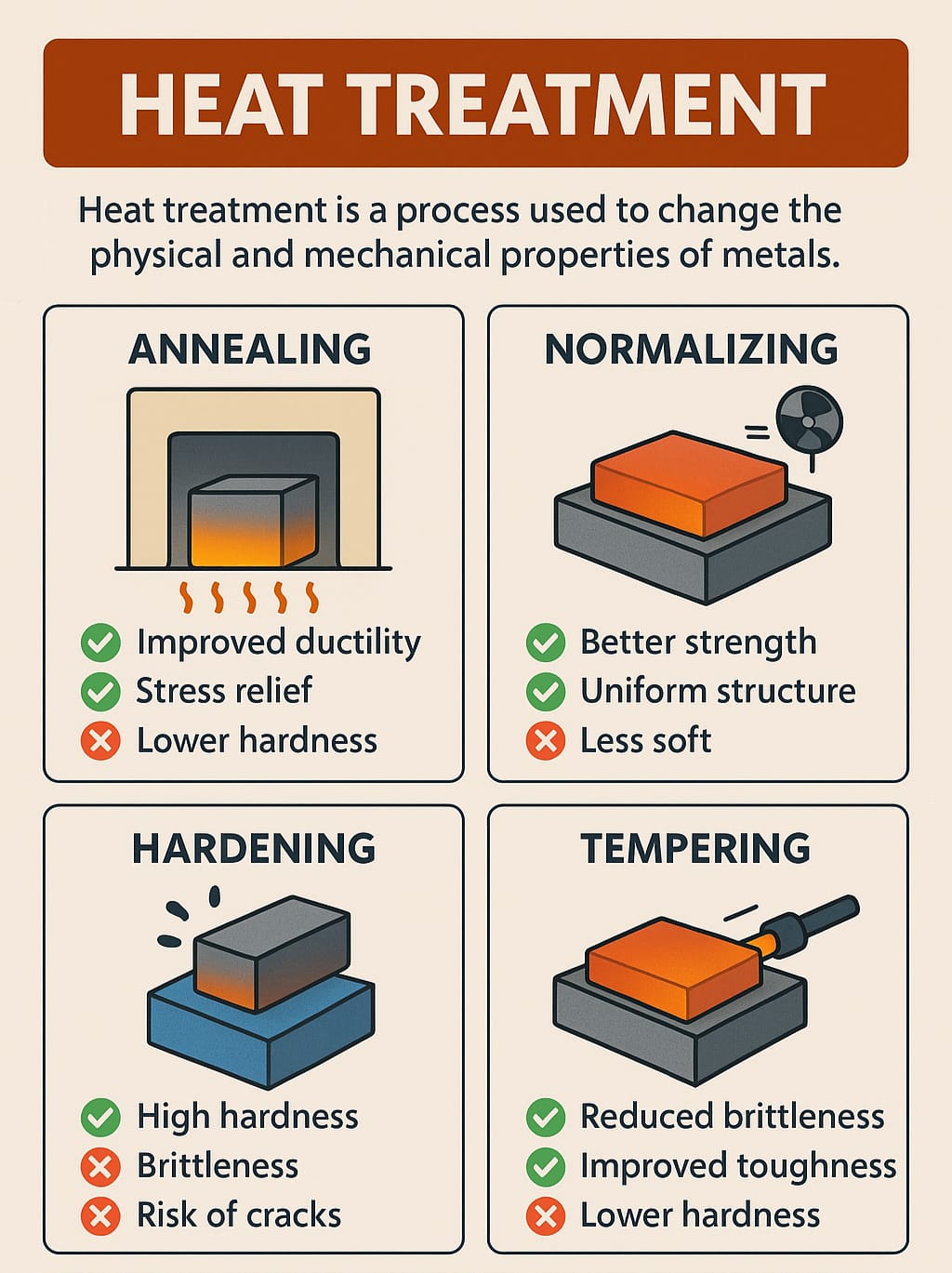
1️⃣ Annealing – For Softening and Stress Relief
Purpose:
- Soften the metal
- Remove internal stresses
Process:
Metal is heated above its recrystallization temperature, held for a certain time, and then slowly cooled (usually inside the furnace).
Requirements:
- Controlled furnace temperature
- Slow cooling medium (e.g. furnace cooling)
Effects:
✅ Improved ductility and machinability
✅ Grain refinement
✅ Stress relief
Drawbacks:
❌ Time-consuming
❌ Lower hardness
💡 Pro Tip: Ideal for cold-worked or highly stressed metal parts.
2️⃣ Normalizing – Grain Refinement and Strength
Purpose:
- Refine grain structure
- Relieve internal stresses
- Improve mechanical properties
Process:
Heat the metal above its critical temperature, hold it, and then cool it in open air.
Requirements:
- Uniform heating
- Air cooling
Effects:
✅ Better strength than annealing
✅ More uniform microstructure
Drawbacks:
❌ Slightly less soft than annealed parts
💡 Pro Tip: Best suited for forgings, castings, and weldments.
3️⃣ Hardening – Maximum Strength and Wear Resistance
Purpose:
- Increase hardness
- Enhance wear resistance
Process:
Heat above the critical temperature and then rapidly quench in oil or water.
Requirements:
- Accurate control of temperature and time
- Correct quenching medium
Effects:
✅ High strength and hardness
❌ Increased brittleness
Drawbacks:
❌ Risk of cracks
❌ Development of internal stresses
💡 Pro Tip: Always follow hardening with tempering to reduce brittleness.
4️⃣ Tempering – Reducing Brittleness
Purpose:
- Reduce brittleness of hardened steel
- Improve toughness
Process:
Reheat the hardened part below the critical temperature, hold it, and then cool it down.
Requirements:
- Precise temperature control based on required properties
Effects:
✅ Better toughness
✅ Stress relief
❌ Slight reduction in hardness
💡 Pro Tip: Select tempering temperature based on the balance between strength and ductility you need.
5️⃣ Case Hardening (Carburizing / Nitriding) – Hard Surface, Tough Core
Purpose:
- Hard wear-resistant surface
- Tough inner core for shock resistance
Process:
Add carbon or nitrogen to the surface of the metal at high temperature, then quench it.
Requirements:
- Controlled atmosphere
- Alloy steels suitable for surface hardening
Effects:
✅ Surface hardness for wear resistance
✅ Core toughness for impact strength
Drawbacks:
❌ Expensive
❌ Requires precise process control
💡 Pro Tip: Perfect for gears, shafts, and tools that require high surface hardness with a ductile core.
✅ Key Takeaway
Heat treatment is the art of balancing strength, hardness, ductility, and microstructure.
- Use Annealing for softening.
- Choose Normalizing for grain refinement.
- Apply Hardening for maximum strength.
- Perform Tempering to reduce brittleness.
- Opt for Case Hardening for surface wear resistance.
By selecting the right heat treatment process, you ensure the best mechanical properties for your components.