🚀 What is Lean Manufacturing?
Lean Manufacturing is a production philosophy that focuses on maximizing value for customers while minimizing waste. The idea is simple — do more with less: less time, less inventory, less space, and fewer resources, while maintaining or improving quality.
Lean principles were originally developed by Toyota and are now widely applied across industries — from automotive and aerospace to healthcare and IT.
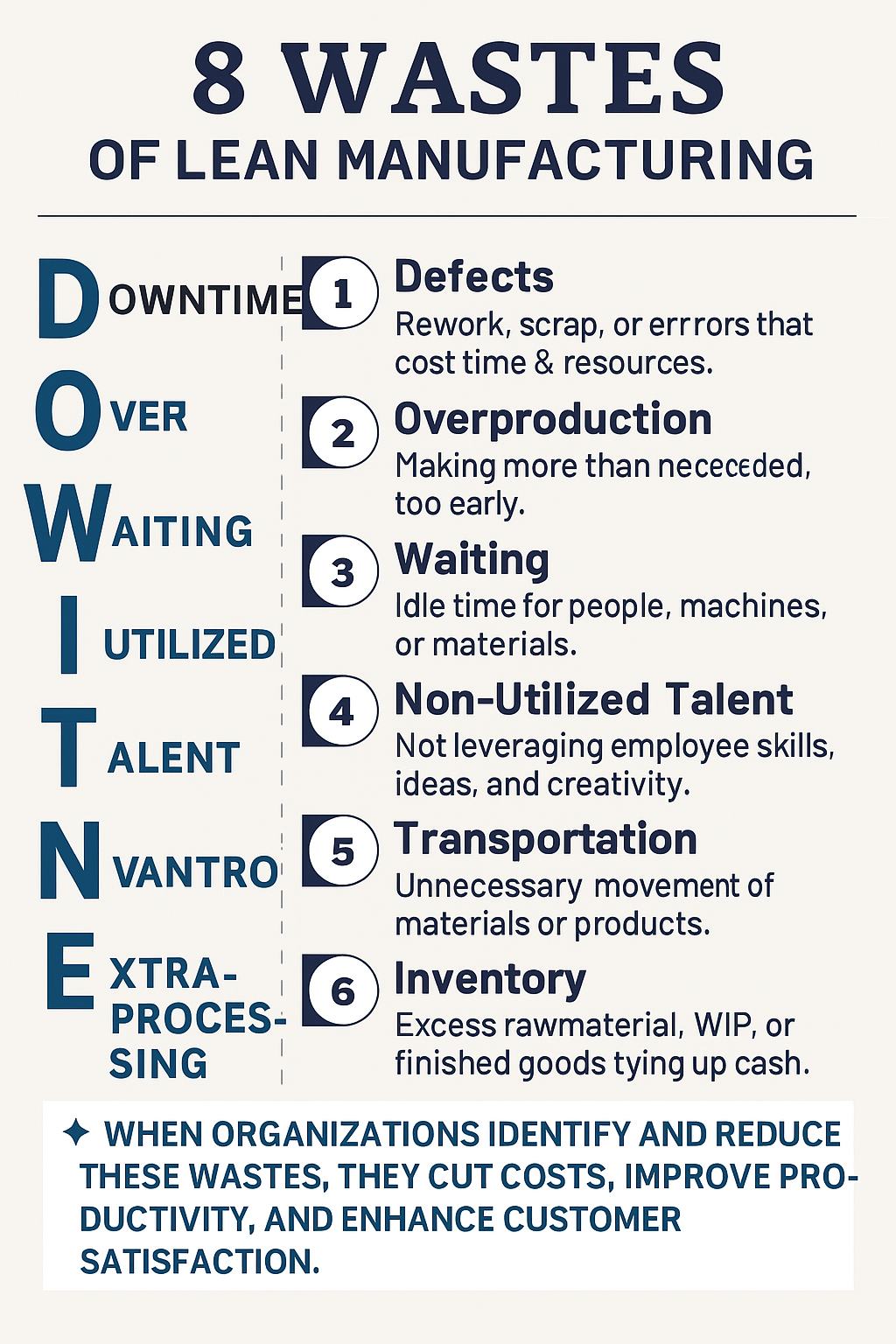
⚙️ Understanding the 8 Wastes of Lean Manufacturing (DOWNTIME)
The eight wastes represent non-value-added activities that drain time, money, and resources from your process.
They can be remembered using the acronym DOWNTIME:
1️⃣ Defects
Mistakes that lead to rework, scrap, or customer complaints.
These result in wasted time, material, and labor.
Example: Incorrect assembly of components that need rework before shipment.
2️⃣ Overproduction
Producing more than what is required — or producing it too early — ties up capital and storage space.
Example: Manufacturing extra parts “just in case,” which may later become obsolete.
3️⃣ Waiting
Idle time when workers, machines, or materials are not being used efficiently.
Example: Operators waiting for raw materials, approvals, or machine setup completion.
4️⃣ Non-Utilized Talent
Failing to use employee creativity, problem-solving skills, or process improvement ideas.
Example: Skilled workers spending time on repetitive, low-value tasks instead of process optimization.
5️⃣ Transportation
Unnecessary movement of materials or products between locations.
Example: Moving parts across long distances within a factory due to poor layout design.
6️⃣ Inventory
Excess raw materials, work-in-progress (WIP), or finished goods that tie up cash and storage space.
Example: Overstocking raw materials that might expire or become obsolete.
7️⃣ Motion
Unnecessary movement of people or equipment that adds no value.
Example: Workers walking back and forth to get tools due to poor workstation layout.
8️⃣ Extra Processing
Performing work or adding features that don’t increase customer value.
Example: Polishing non-visible parts or over-engineering components.
🌟 Benefits of Eliminating Waste
By identifying and reducing these 8 wastes, organizations can:
- Increase productivity and throughput
- Improve quality and reduce costs
- Shorten lead times
- Enhance employee engagement
- Deliver greater customer satisfaction
🧩 Final Thoughts
Eliminating waste is at the heart of Lean Manufacturing. When companies focus on continuous improvement (Kaizen) and actively involve their teams in spotting and solving inefficiencies, they not only save costs but also build a culture of excellence.
📖 Read More on Lean & Quality Topics:
- Root Cause Analysis (RCA): Process & Key Steps Explained
- 5S Methodology: The Foundation of Lean Manufacturing
💡 Written by: JobDrive47 Editorial Team
💼 Category: Lean Manufacturing | Process Improvement | Engineering